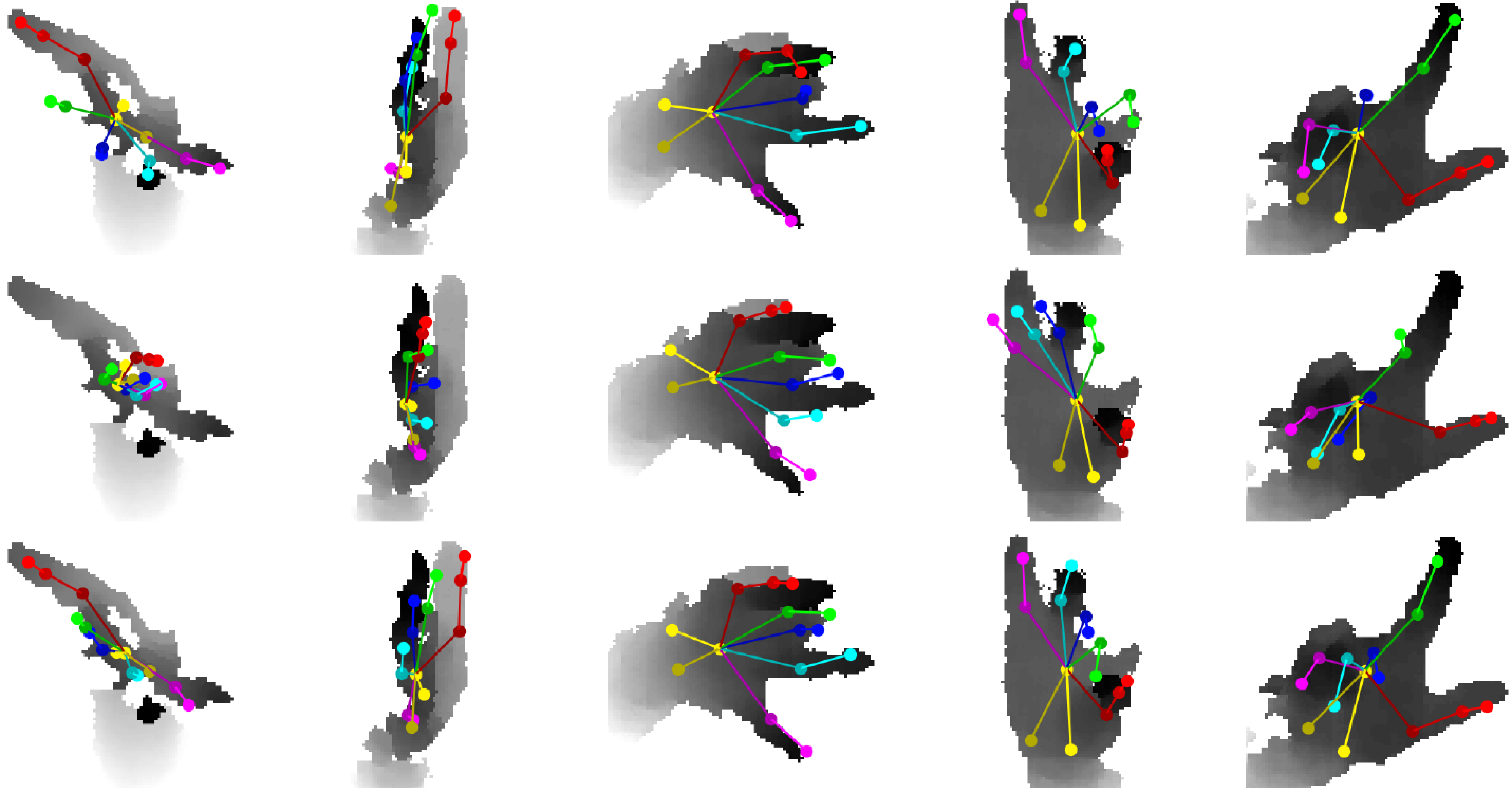
We introduce a method to exploit unlabeled data, which improves results
especially for highly distorted images and difficult poses.
Top: ground truth. Middle: baseline trained with labeled data (synthetic and 100 real).
Bottom: our result from training with the same labeled data and additional unlabeled real data.
Abstract
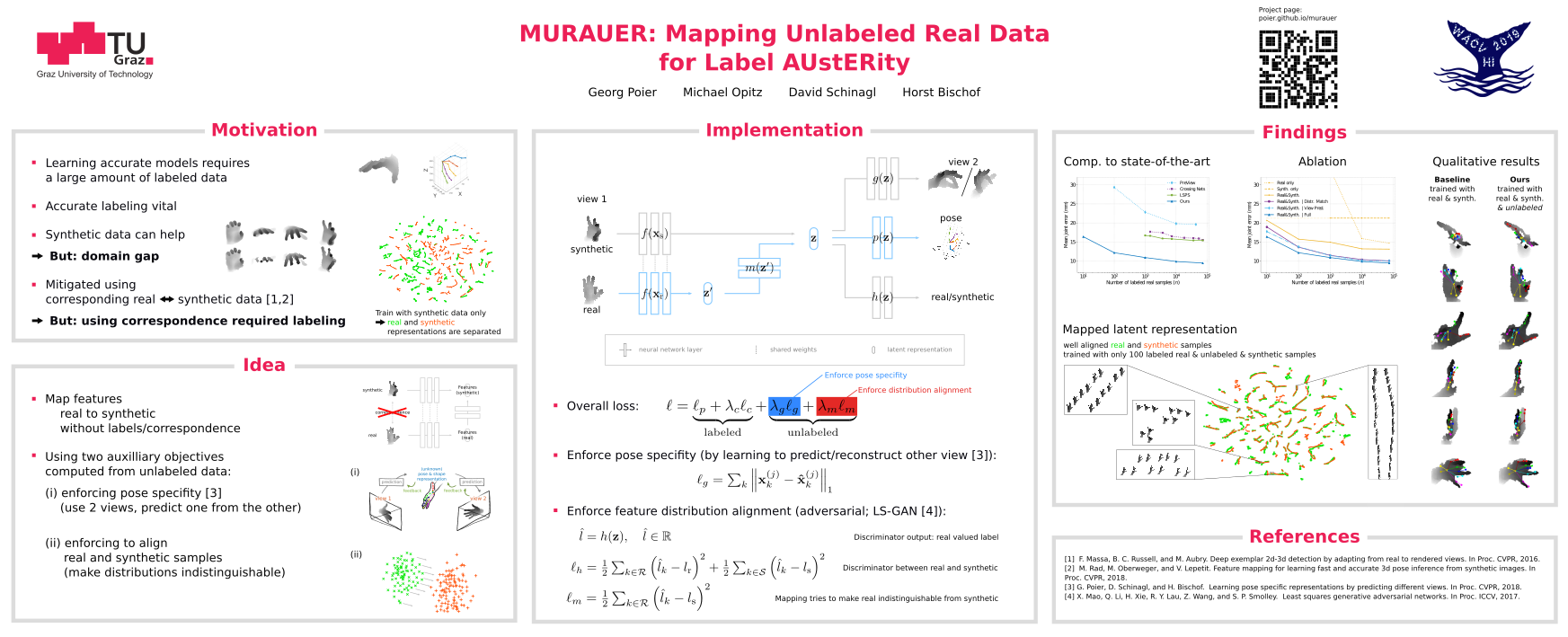
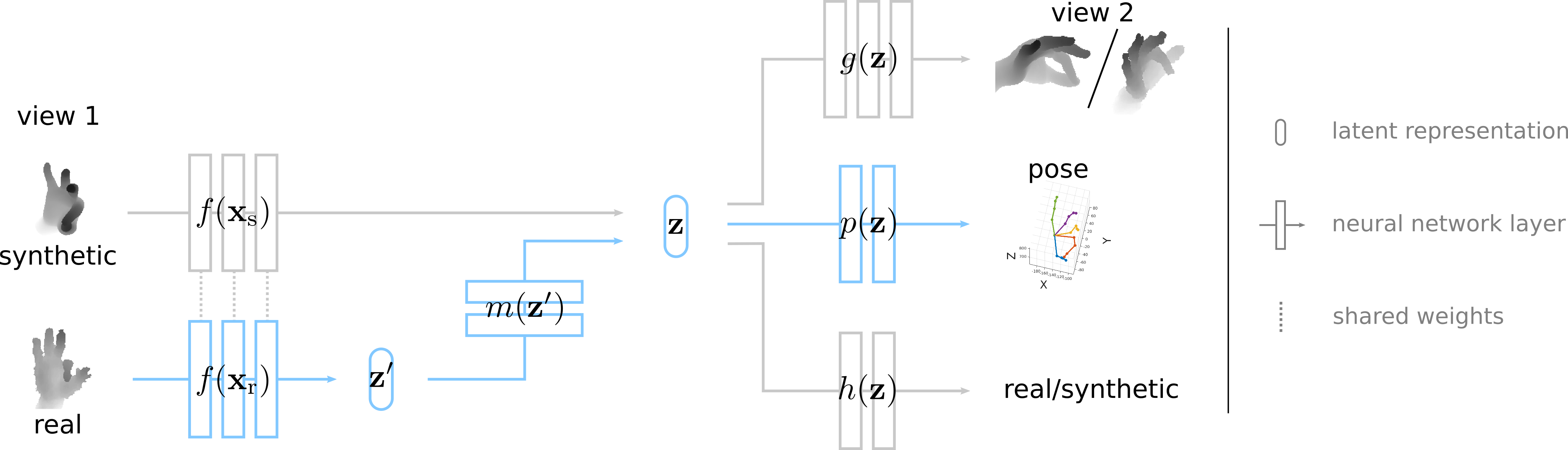
Data labeling for learning 3D hand pose estimation models is a huge effort. Readily available, accurately labeled synthetic data has the potential to reduce the effort. However, to successfully exploit synthetic data, current state-of-the-art methods still require a large amount of labeled real data. In this work, we remove this requirement by learning to map from the features of real data to the features of synthetic data mainly using a large amount of synthetic and unlabeled real data. We exploit unlabeled data using two auxiliary objectives, which enforce that (i) the mapped representation is pose specific and (ii) at the same time, the distributions of real and synthetic data are aligned. While pose specifity is enforced by a self-supervisory signal requiring that the representation is predictive for the appearance from different views, distributions are aligned by an adversarial term. In this way, we can significantly improve the results of the baseline system, which does not use unlabeled data and outperform many recent approaches already with about 1% of the labeled real data. This presents a step towards faster deployment of learning based hand pose estimation, making it accessible for a larger range of applications.
Paper
MURAUER: Mapping Unlabeled Real Data for Label AUstERity.
In WACV 2019.
[Paper & Supp. (arXiv)]
[Paper (IEEE Xplore; original IEEE publication)]
[Paper as webpage] provided by arxiv-vanity.com. Not perfect (e.g., some figures are assembled wrongly) but probably still easier to read on some devices.
Poster
[Poster] presented at WACV 2019.
Code
[Code] at github
Results
Below you find text files with predicted joint positions for the NYU dataset (for different numbers of labeled real samples, n, used for training).
| n | Joint positions (uvd) | Joint positions (xyz) | Mean error (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | n10-uvd | n10-xyz | 16.4 |
| 100 | n100-uvd | n100-xyz | 12.2 |
| 1,000 | n1k-uvd | n1k-xyz | 10.9 |
| 10,000 | n10k-uvd | n10k-xyz | 9.9 |
| 72,757 | n73k-uvd | n73k-xyz | 9.5 |
Citation
If you can make use of this work, please cite:
MURAUER: Mapping Unlabeled Real Data for Label AUstERity.
Georg Poier, Michael Opitz, David Schinagl and Horst Bischof.
In Proc. WACV, 2019.
Bibtex:
@inproceedings{Poier2019wacv_murauer,
author = {Georg Poier and Michael Opitz and David Schinagl and Horst Bischof},
title = {{MURAUER}: Mapping Unlabeled Real Data for Label AUstERity},
booktitle = {{Proc. IEEE Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)}},
year = {2019}
}
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their effort and valuable feedback, and Markus Oberweger for his feedback regarding their implementation of [Feature Mapping].